Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, providing them with unparalleled scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, as organizations increasingly rely on the cloud for their critical infrastructure and applications, the need for effective cloud monitoring and management architecture becomes paramount. In this article, we will explore the key components and best practices of cloud monitoring and management architecture, enabling businesses to optimize their cloud environments while ensuring data security and operational efficiency.
Understanding Cloud Monitoring and Management
In today’s digital landscape, businesses are increasingly leveraging the power of the cloud to drive innovation and agility. Cloud monitoring and management play a crucial role in ensuring that these cloud-based resources are operating optimally. Cloud monitoring involves the continuous observation and measurement of cloud infrastructure, applications, and services to identify performance bottlenecks, potential security threats, and other issues that may impact the availability and reliability of the cloud environment. On the other hand, cloud management encompasses the proactive administration and optimization of cloud resources, including capacity planning, resource allocation, and cost management.
The Role of Monitoring Tools
Effective cloud monitoring requires robust monitoring tools that provide real-time visibility into the performance and health of the cloud environment. These tools collect and analyze data from various sources, such as logs, metrics, and events, allowing organizations to detect anomalies, troubleshoot issues, and make informed decisions based on actionable insights. Some popular cloud monitoring tools include Amazon CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, and Google Cloud Monitoring.
The Importance of Proactive Management
Proactive cloud management is crucial for maintaining a robust and efficient cloud infrastructure. It involves regular monitoring, analysis, and optimization of cloud resources to ensure optimal performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. By proactively identifying and addressing potential issues, organizations can minimize downtime, improve resource utilization, and deliver a seamless user experience.
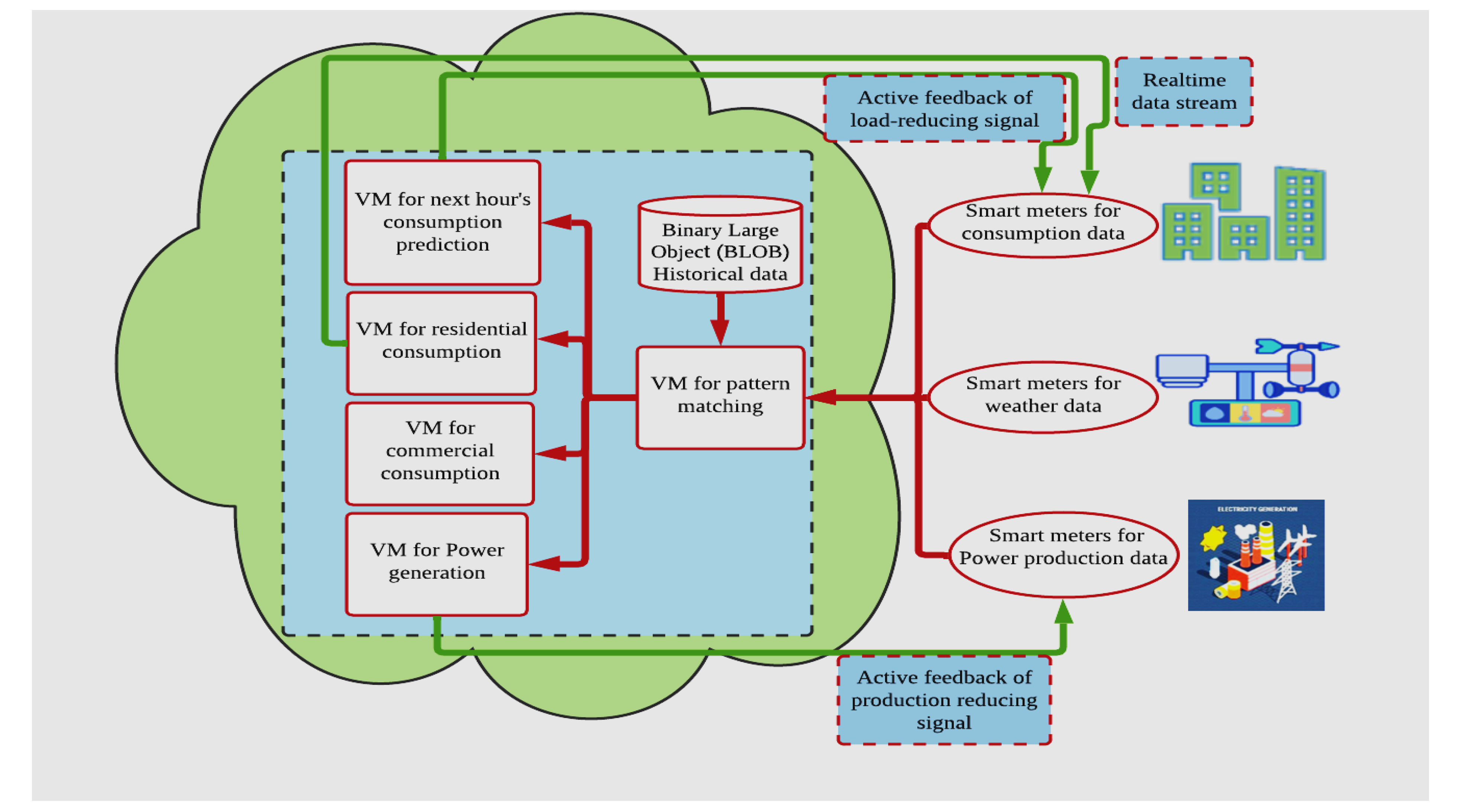
The Components of Cloud Monitoring and Management Architecture
A comprehensive cloud monitoring and management architecture consists of several key components that work together to provide organizations with the necessary visibility and control over their cloud environments.
Real-time Monitoring
Real-time monitoring is a critical component of cloud monitoring and management architecture. It involves the continuous collection and analysis of performance metrics, logs, and events to provide organizations with up-to-date information about the health and performance of their cloud resources. Real-time monitoring enables proactive incident response, rapid troubleshooting, and the ability to scale resources dynamically based on demand.
Log Analysis
Logs contain a wealth of information about the behavior and performance of cloud resources. Effective log analysis involves the aggregation, parsing, and analysis of logs from various sources to identify patterns, anomalies, and potential security threats. By analyzing logs, organizations can gain insights into system behavior, detect performance bottlenecks, and enhance security by identifying suspicious activities.
Performance Metrics
Performance metrics provide organizations with quantitative data about the performance and utilization of their cloud resources. These metrics include CPU usage, memory utilization, network throughput, and response times. By monitoring and analyzing performance metrics, organizations can identify resource bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and ensure optimal performance even during peak usage periods.
Automation and Alerting Systems
Automation and alerting systems play a crucial role in effective cloud monitoring and management. Automation enables organizations to streamline monitoring processes, automate routine tasks, and respond to incidents promptly. Alerting systems notify administrators and stakeholders about critical events and anomalies, allowing them to take immediate action to resolve issues and minimize downtime.
Ensuring Data Security in the Cloud
Data security is a top concern for businesses migrating to the cloud. While cloud service providers offer robust security measures, organizations must also implement additional security measures within their cloud monitoring and management architecture to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Encryption
Encryption is a fundamental security measure that helps protect data transmitted and stored in the cloud. By encrypting data at rest and in transit, organizations can ensure that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains unintelligible. Implementing strong encryption algorithms and key management practices is essential to maintaining data security in the cloud.
Access Controls
Implementing robust access controls is crucial for preventing unauthorized access to cloud resources. Organizations should enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, and implement fine-grained access controls to limit access to sensitive data and resources. Regularly reviewing and updating access control policies is essential to mitigate the risk of data breaches.
Threat Detection
Cloud monitoring and management architecture should include robust threat detection mechanisms to identify and respond to potential security threats. This can be achieved through the implementation of intrusion detection and prevention systems, anomaly detection algorithms, and continuous monitoring of network traffic and user behavior patterns. Promptly detecting and responding to security threats is vital for minimizing the impact of potential breaches.
Scalability and Resource Optimization in the Cloud
The cloud offers unparalleled scalability, allowing organizations to scale their resources dynamically based on demand. However, to fully leverage this scalability and optimize resource allocation, organizations must incorporate scalability and resource optimization strategies within their cloud monitoring and management architecture.
Dynamic Resource Scaling
Dynamic resource scaling enables organizations to automatically adjust resource allocation based on demand. By monitoring performance metrics and setting up policies, organizations can scale resources up or down in real-time, ensuring that resources are available when needed and minimizing unnecessary costs during periods of low demand.
Capacity Planning
Capacity planning involves forecasting future resource requirements based on historical usage patterns and projected growth. By accurately predicting resource needs, organizations can plan for capacity upgrades or downsizing in advance, avoiding resource constraints and ensuring optimal performance.
Cost Optimization
Cloud cost optimization is crucial for organizations aiming to maximize the value of their cloud investments. By monitoring resource utilization, identifying idle resources, and leveraging cost-saving options provided by cloud service providers, organizations can optimize their cloud spending and achieve significant cost savings.
Cloud Monitoring and Management Tools
A wide range of cloud monitoring and management tools are available in the market, each offering unique features and capabilities. Choosing the right tool for your organization depends on factors such as budget, cloud service provider, and specific monitoring requirements.
Amazon CloudWatch
Amazon CloudWatch is a popular cloud monitoring and management tool designed specifically for Amazon Web Services (AWS) environments. It provides comprehensive monitoring of AWS resources, collects and analyzes logs and metrics, and enables proactive resource optimization and cost management.
Azure Monitor
Azure Monitor is Microsoft’s cloud monitoring and management solution for Azure environments. It offers real-time monitoring, log analytics, and performance metrics for Azure resources. Azure Monitor integrates with other Azure services and provides advanced capabilities for managing and optimizing Azure deployments.
Google Cloud Monitoring
Google Cloud Monitoring is Google’s monitoring and management tool for Google Cloud Platform (GCP) environments. It offers real-time monitoring, log analysis, and performance metrics for GCP resources. Google Cloud Monitoring provides integration with other GCP services and enables organizations to gain deep insights into the health and performance of their GCP deployments.
Best Practices for Cloud Monitoring and Management
Implementing best practices for cloud monitoring and management is essential to ensure the effectiveness and efficiency of your cloud environment. By following these best practices, organizations can optimize their monitoring strategy, improve incident response time, and enhance overall operational performance.
Establish Clear Monitoring Objectives
Before implementing a cloud monitoring and management architecture, it is crucial to define clear and measurable monitoring objectives. Determine the key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with your organization’s goals and ensure that your monitoring strategy focuses on measuring and optimizing these KPIs.
Set Up Effective Alerting Systems
Alerting systems play a critical role in incident response and minimizing downtime. Configure alerting systems to notify the appropriate stakeholders when predefined thresholds are breached or anomalies are detected. Ensure that alerts are actionable, provide sufficient context, and are sent to the right individuals or teams.
Regularly Review and Optimize Monitoring Strategy
Cloud environments are dynamic, and monitoring requirements may change over time. Regularly review and optimize your monitoring strategy to ensure that it aligns with your organization’s evolving needs. Analyze monitoring data, identify areas for improvement, and adjust your monitoring approach accordingly.
Case Studies: Successful Cloud Monitoring and Management Implementations
Real-world examples of successful cloud monitoring and management implementations can provide valuable insights and inspiration for organizations looking to optimize their cloud environments. Let’s explore a few case studies that highlight the benefits and challenges of implementing effective cloud monitoring and management architectures.
Case Study 1: Company X’s Journey to Proactive Cloud Monitoring
Company X, a leading e-commerce platform, experienced frequent downtime and performance issues in their cloud environment. Recognizing the need for proactive monitoring, they implemented a comprehensive cloud monitoring and management architecture. By leveraging real-time monitoring, log analysis, and automation, Company X was able to detect and resolve issues before they impacted their customers. The result was improved uptime, enhanced customer satisfaction, and increased revenue.
Case Study 2: Organization Y’s Cost Optimization Journey
Organization Y, a growing SaaS company, realized that theirexisting cloud environment was costing them more than anticipated. Through a thorough analysis of their resource utilization and cost patterns, they identified areas of inefficiency and implemented a robust cloud monitoring and management architecture. By leveraging dynamic resource scaling, capacity planning, and cost optimization strategies, Organization Y was able to optimize their resource allocation, reduce unnecessary costs, and achieve significant savings in their cloud spending. This allowed them to invest those savings back into their business and fuel further growth.
Challenges and Future Trends in Cloud Monitoring and Management
The cloud landscape is constantly evolving, presenting new challenges and opportunities for organizations in their cloud monitoring and management efforts. Understanding these challenges and staying informed about the latest trends can help organizations stay ahead and ensure their cloud environments are efficient, secure, and future-proof.
Challenge 1: Complexity of Multi-Cloud Environments
Many organizations operate in multi-cloud environments, leveraging different cloud service providers for various business needs. Managing and monitoring these diverse environments can be challenging, as each cloud provider may have its own monitoring tools and APIs. Organizations must invest in solutions that can provide a unified view of their multi-cloud infrastructure and enable seamless monitoring and management across different providers.
Challenge 2: Ensuring Compliance in the Cloud
As more organizations handle sensitive data in the cloud, ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations becomes paramount. Cloud monitoring and management architectures must incorporate robust security measures and compliance controls to meet regulatory requirements. This includes implementing strong access controls, encryption, and regularly auditing the cloud environment to ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Challenge 3: Managing Big Data and Analytics
The exponential growth of data in the cloud presents challenges in terms of managing and analyzing vast amounts of information. Organizations need to leverage cloud monitoring and management architectures that can handle the volume, variety, and velocity of data generated by their cloud resources. This may involve implementing scalable data storage solutions, leveraging big data analytics tools, and integrating machine learning algorithms to gain actionable insights from the data.
Future Trend 1: AI-Driven Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI)-driven analytics is poised to play a significant role in cloud monitoring and management. By leveraging machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics, organizations can gain deeper insights into their cloud environment’s performance, detect anomalies, and proactively address potential issues. AI-driven analytics can also help automate routine monitoring tasks, freeing up resources for more strategic initiatives.
Future Trend 2: Serverless Architectures
Serverless architectures, where organizations deploy their applications without managing underlying servers, are gaining popularity due to their scalability and cost-efficiency. Cloud monitoring and management architectures must adapt to this trend by providing monitoring capabilities specifically designed for serverless environments. This includes monitoring function invocations, response times, and resource utilization within a serverless context.
Future Trend 3: Edge Computing
Edge computing, where data processing and analysis occur closer to the data source, is emerging as a powerful paradigm in the cloud landscape. With edge computing, organizations can reduce latency, improve data privacy, and enhance real-time decision-making. Cloud monitoring and management architectures need to evolve to accommodate edge computing infrastructures, providing real-time monitoring and analysis capabilities at the edge.
Conclusion
A well-designed cloud monitoring and management architecture is vital for organizations looking to maximize the benefits of the cloud while ensuring security, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. By understanding the key components, best practices, and emerging trends in cloud monitoring and management, organizations can build robust architectures that enable seamless operation of their cloud environments. From real-time monitoring and log analysis to ensuring data security and optimizing resource allocation, organizations must prioritize proactive monitoring and efficient management to reap the rewards of a well-managed cloud infrastructure. Stay informed, stay proactive, and embrace the evolving technologies and trends that shape the future of cloud monitoring and management.