In today’s digital era, businesses are increasingly relying on cloud computing to store and access their data. As a result, cloud network architecture has become a crucial component for ensuring seamless connectivity, security, and scalability. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of cloud network architecture, exploring its key concepts, benefits, and best practices. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or an entrepreneur looking to leverage the power of the cloud, this article will provide you with invaluable insights to optimize your network infrastructure.
Introduction to Cloud Network Architecture
Cloud network architecture refers to the design and structure of a network system that facilitates the operation and management of cloud computing services. Unlike traditional network setups, cloud network architecture leverages the power of virtualization and software-defined networking (SDN) to create a flexible, scalable, and agile infrastructure.
Cloud network architecture can be deployed in various forms, including public, private, and hybrid clouds. Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party service providers, offering resources and services to multiple organizations. Private clouds, on the other hand, are dedicated to a single organization, providing enhanced control and security. Hybrid clouds combine the benefits of both public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the scalability of public clouds while maintaining sensitive data in private clouds.
Key Components of Cloud Network Architecture
1. Virtualization
Virtualization is a fundamental component of cloud network architecture. It involves creating virtual instances of servers, storage, and networking resources, allowing for the efficient utilization of physical hardware. By abstracting the underlying infrastructure, virtualization enables the dynamic allocation and provisioning of resources, resulting in improved scalability and flexibility.
2. Networking Protocols
Networking protocols play a vital role in cloud network architecture, enabling communication between various components and systems. Protocols such as TCP/IP, VLAN, and MPLS facilitate the transmission of data packets across the network, ensuring reliable and secure connectivity. Additionally, protocols like BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) enable seamless integration with external networks, enabling organizations to extend their cloud network architecture beyond the confines of their own infrastructure.
3. Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) is a paradigm that separates the control plane from the data plane in network architecture. In cloud network architecture, SDN enables centralized management and control of network resources through software-based controllers. This decoupling of control and data planes allows for more efficient network administration, simplified network provisioning, and the ability to dynamically adapt to changing traffic patterns.
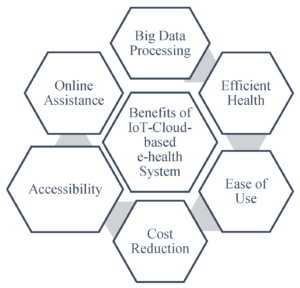
Benefits of Cloud Network Architecture
The adoption of cloud network architecture offers numerous benefits for organizations:
1. Cost Savings
Cloud network architecture eliminates the need for organizations to invest in costly hardware infrastructure. Instead, they can leverage the resources provided by cloud service providers on a pay-as-you-go basis. This significantly reduces capital expenditures, allowing organizations to allocate their resources more efficiently.
2. Increased Agility
With cloud network architecture, organizations can quickly scale their resources up or down based on demand. The ability to provision and deprovision resources on the fly enables businesses to respond rapidly to changing market conditions and customer needs.
3. Improved Security
Cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures to protect their infrastructure and customer data. By leveraging cloud network architecture, organizations can benefit from enhanced security features such as encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems. These measures help mitigate the risk of data breaches and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
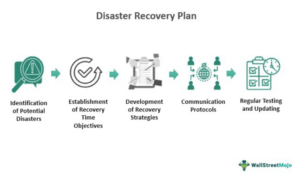
4. Disaster Recovery
Cloud network architecture provides built-in disaster recovery capabilities, offering organizations the ability to replicate their data and applications across multiple geographical locations. In the event of a disaster or system failure, organizations can quickly recover their operations and minimize downtime, ensuring business continuity.
Designing a Secure Cloud Network
1. Network Segmentation
Network segmentation involves dividing the network into smaller, isolated segments to enhance security. By implementing proper segmentation, organizations can limit the lateral movement of threats and contain potential breaches.
2. Access Controls
Implementing strong access controls is essential to secure a cloud network architecture. Organizations should enforce strict authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to ensure that only authorized users can access the network resources.
3. Encryption
Encrypting data in transit and at rest is crucial for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of information in a cloud network architecture. By leveraging encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, organizations can protect their data from unauthorized access or interception.
4. Intrusion Detection Systems
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) play a critical role in identifying and mitigating potential security threats in a cloud network architecture. IDS monitors network traffic, looking for anomalies and suspicious activities, and alerts administrators to take appropriate action.
Scalability and Elasticity in Cloud Network Architecture
Scalability and elasticity are key features of cloud network architecture that enable organizations to meet varying demands efficiently:
1. Load Balancing
Load balancing is a technique that distributes network traffic evenly across multiple servers or resources. By distributing the workload, load balancing ensures optimal resource utilization and prevents any single component from becoming a bottleneck.
2. Auto-Scaling
Auto-scaling allows organizations to automatically adjust their resource capacity based on demand. By monitoring metrics such as CPU utilization or network traffic, auto-scaling mechanisms can dynamically add or remove resources to match the workload, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
3. Containerization
Containerization is a lightweight virtualization technology that allows applications to run in isolated environments called containers. Containers provide a consistent runtime environment, making it easier to deploy and scale applications in a cloud network architecture.
4. Resource Utilization Monitoring
Monitoring resource utilization is vital for optimizing a cloud network architecture. By continuously monitoring metrics such as CPU usage, memory utilization, and network throughput, organizations can identify inefficiencies and make informed decisions to improve resource allocation and performance.
Network Virtualization in Cloud Architectures
1. Virtual LANs (VLANs)
Virtual LANs (VLANs) enable the segmentation of a physical network into multiple logical networks. By isolating traffic between VLANs, organizations can achieve improved network performance, increased security, and simplified management.
2. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) provide secure connectivity over public networks such as the internet. By creating encrypted tunnels, VPNs ensure the confidentiality and integrity of data transmitted between remote locations or users accessing the cloud network architecture.
3. Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
Network Function Virtualization (NFV) is a technology that enables the virtualization of network functions such as firewalls, routers, and load balancers. By replacing dedicated hardware appliances with software-based equivalents, organizations can achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings in their cloud network architecture.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider
When selecting a cloud service provider for your cloud network architecture, consider the following factors:
1. Reliability and Performance
Ensure that the cloud service provider has a robust infrastructure with high availability and low latency. Look for providers that offer service level agreements (SLAs) guaranteeing uptime and performance.
2. Data Sovereignty
If your organization operates in a region with strict data privacy regulations, ensure that the cloud service provider complies with the necessary data protection laws. Verify that data is stored and processed in locations that align with your legal requirements.
3. Service Offerings
Consider the range of services and features offered by the cloud service provider. Assess whether they align with your organization’s specific needs and requirements. Look for providers that offer a comprehensive suite of services, including compute, storage, networking, and security.
4. Cost and Pricing Model
Evaluate the pricing structure of the cloud service provider. Consider factors such as upfront costs, usage-based pricing, and any additional charges for data transfer or storage. Ensure that the pricing model aligns with your organization’s budget and cost expectations.
Case Studies: Successful Cloud Network Implementations
Examining real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the benefits and challenges of implementing cloud network architectures:
1. Company XYZ: Cloud Network Migration
Company XYZ, a multinational corporation, successfully migrated its on-premises infrastructure to a public cloud network architecture. By leveraging the scalability and flexibility of the cloud, they achieved significant cost savings, improved agility, and enhanced scalability. Additionally, the company implemented robust security measures, including network segmentation and encryption, to protect their sensitive data.
2. Startup ABC: Hybrid Cloud Network Architecture
Startup ABC implemented a hybrid cloud network architecture, combining a private cloud for their critical business applications and a public cloud for non-sensitive workloads. This approach allowed them to maintain control over their sensitive data while leveraging the scalability and costefficiency of public cloud resources. By implementing load balancing and auto-scaling mechanisms, they were able to handle sudden spikes in traffic and ensure optimal performance for their customers.
3. Organization DEF: Cloud Network Security
Organization DEF, a healthcare provider, adopted a private cloud network architecture to meet their strict data privacy and security requirements. They implemented robust access controls, encryption, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard patient data. By leveraging network virtualization and segmentation, they achieved enhanced security and compliance while maintaining seamless connectivity across their network.
Future Trends in Cloud Network Architecture
Cloud network architecture continues to evolve, driven by emerging technologies and industry trends:
1. Edge Computing
Edge computing is a paradigm that brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. By processing data at the edge of the network, organizations can reduce latency and improve the performance of cloud applications and services.
2. 5G Networks
The rollout of 5G networks promises faster speeds and lower latency, enabling organizations to leverage cloud network architecture for real-time applications and services. With increased bandwidth and reliability, 5G networks will revolutionize the way data is transmitted and processed in the cloud.
3. Serverless Computing
Serverless computing, also known as Function as a Service (FaaS), allows developers to focus on writing code without the need to manage underlying infrastructure. By abstracting away servers and resources, organizations can achieve greater agility and cost efficiency in their cloud network architecture.
4. Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming cloud network architecture by enabling intelligent automation, predictive analytics, and enhanced security. AI-powered networking solutions can optimize network traffic, detect anomalies, and automate network management tasks, improving overall performance and efficiency.
Best Practices for Cloud Network Management
Efficient management is crucial for optimizing the performance and security of a cloud network architecture:
1. Network Monitoring
Implement robust network monitoring tools to track the performance, availability, and security of your cloud network architecture. Monitor key metrics such as bandwidth utilization, latency, and packet loss to identify potential issues and proactively address them.
2. Performance Optimization
Regularly assess the performance of your cloud network architecture and identify areas for improvement. Optimize network configurations, implement caching mechanisms, and leverage content delivery networks (CDNs) to enhance the responsiveness and speed of your cloud applications.
3. Troubleshooting
Develop a structured troubleshooting approach to quickly identify and resolve network issues. Use network diagnostic tools, analyze logs, and engage with your cloud service provider’s support team to efficiently troubleshoot and resolve any network-related problems.
4. Capacity Planning
Monitor resource utilization trends and plan for future capacity requirements. Understand the growth patterns of your applications and services and ensure that your cloud network architecture can scale accordingly. Regularly review and adjust your resource allocation to optimize costs and performance.
In conclusion, understanding cloud network architecture is essential for organizations seeking to leverage the power of the cloud. By adopting the right strategies, implementing robust security measures, and harnessing the scalability and flexibility of the cloud, businesses can enhance their agility, reduce costs, and drive innovation. Stay ahead of the curve by keeping up with emerging trends and continuously optimizing your cloud network architecture. Embrace the cloud, and unlock the limitless potential it offers for your organization.