Welcome to our comprehensive guide on cloud security architecture. In today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber attacks are on the rise, it is crucial for businesses to prioritize the security of their cloud infrastructure. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of cloud security architecture, exploring its importance, key components, and best practices. Whether you are a business owner, IT professional, or simply interested in understanding the foundations of cloud security, this guide is for you.
Introduction to Cloud Security Architecture
In this section, we will provide an overview of cloud security architecture, explaining its role in protecting data and applications in the cloud. We will discuss the fundamental principles and concepts that underpin this architecture, giving you a solid foundation to build upon.
What is Cloud Security Architecture?
Cloud security architecture refers to the design and implementation of security measures within a cloud computing environment. It aims to protect data, applications, and infrastructure from unauthorized access, data breaches, and other security threats. Cloud security architecture encompasses various components and strategies that work together to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of cloud resources.
The Importance of Cloud Security Architecture
With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, organizations are entrusting their sensitive data and critical applications to third-party cloud service providers. This shift requires a robust security framework to address the unique challenges and risks associated with the cloud. Cloud security architecture provides organizations with the necessary tools and strategies to protect their assets, maintain regulatory compliance, and build trust with their customers.
Fundamental Principles of Cloud Security Architecture
Cloud security architecture is built upon several fundamental principles that guide its design and implementation. These principles include:
- Defense in depth: This principle emphasizes the need for multiple layers of security controls to provide comprehensive protection against threats.
- Least privilege: Users and processes should only be granted the minimum privileges necessary to perform their functions, reducing the potential impact of a security breach.
- Data encryption: Encryption ensures that data remains secure, both at rest and in transit, by rendering it unreadable to unauthorized individuals.
- Continuous monitoring: Regular monitoring and analysis of cloud resources enable the detection and mitigation of potential security incidents.
- Resilience and redundancy: Cloud security architecture should include measures to ensure the availability and continuity of services, even in the face of disruptions or attacks.
Cloud Security Threats and Challenges
Understanding the threats and challenges faced by cloud environments is crucial for designing an effective security architecture. In this section, we will explore the various risks associated with cloud computing, including data breaches, insider threats, and DDoS attacks. By being aware of these challenges, you can develop strategies to mitigate them.
Data Breaches in the Cloud
Data breaches pose a significant threat to cloud environments, as they can lead to the exposure of sensitive information and financial losses for organizations. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure, misconfigurations, or weak authentication mechanisms to gain unauthorized access to data. Organizations must implement strong access controls, encryption, and regular vulnerability assessments to minimize the risk of data breaches.
Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to security risks posed by individuals within an organization who have authorized access to cloud resources. These individuals may intentionally or inadvertently misuse their privileges, leading to data leaks, unauthorized access, or sabotage. Implementing strict access controls, monitoring user activities, and conducting regular security awareness training can help mitigate insider threats.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
DDoS attacks aim to overwhelm a cloud service or application with a flood of traffic, rendering it unavailable to legitimate users. These attacks can disrupt business operations, cause financial losses, and damage an organization’s reputation. Cloud security architecture should include measures such as traffic filtering, rate limiting, and load balancing to mitigate the impact of DDoS attacks.
Other Cloud Security Challenges
In addition to the above threats, cloud environments face a range of other security challenges. These include shared responsibility models, vendor lock-in, compliance requirements, and managing security across multiple cloud providers. Organizations must address these challenges through effective security policies, contractual agreements, and the use of security tools and technologies.
Key Components of Cloud Security Architecture
Building a robust cloud security architecture requires careful consideration of its key components. In this section, we will delve into the essential elements that make up a secure cloud infrastructure, such as identity and access management, encryption, and network security. By understanding these components, you can design a comprehensive security framework.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a critical component of cloud security architecture. It involves the management of user identities, authentication, and authorization processes. IAM ensures that only authorized individuals can access cloud resources and that their access privileges are appropriate for their roles. Implementing strong authentication mechanisms, role-based access controls, and multi-factor authentication enhances the security of the cloud environment.
Data Encryption
Data encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information stored in the cloud. Encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, which can only be deciphered with the correct decryption key. Cloud security architecture should include mechanisms for encrypting data at rest and in transit, ensuring that even if unauthorized individuals gain access to the data, they cannot decipher its content.
Network Security
Network security is essential in cloud environments to protect data as it moves between cloud resources and users. This component of cloud security architecture involves the implementation of firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and virtual private networks (VPNs). These measures help prevent unauthorized access, detect and respond to network-based attacks, and secure data transmissions.
Vulnerability Management
Vulnerability management is a proactive approach to identifying and mitigating security vulnerabilities in cloud environments. It involves regular scanning and assessment of cloud resources to identify potential weaknesses. By conducting vulnerability assessments and promptly addressing identified vulnerabilities, organizations can reduce the risk of exploitation by attackers.
Security Incident Response
A robust cloud security architecture should include a well-defined incident response plan. This plan outlines the steps to be taken in the event of a security incident, such as a data breach or a system compromise. It includes procedures for detecting, containing, investigating, and recovering from security incidents. Implementing an effective incident response plan helps minimize the impact of security breaches and facilitates timely recovery.
Best Practices for Cloud Security Architecture
Implementing best practices is vital to ensure the effectiveness of your cloud security architecture. In this section, we will provide you with practical tips and recommendations to enhance the security of your cloud environment. From regular audits to multi-factor authentication, we will cover the strategies that can help safeguard your data and applications.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Performing regular security audits and assessments is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance gaps in your cloud environment. By conducting comprehensive assessments, you can proactively address security issues and ensure that your security controls are effective.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Implementing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your cloud environment. By requiring users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device, you significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised.
Secure Configuration Management
Ensuring that cloud resources are securely configured is vital for maintaining a strong security posture. Implementing secure configuration management practices involves hardening operating systems, disabling unnecessary services, and regularly updating and patching software. By following secure configuration guidelines provided by cloud service providers, you can mitigate many common security risks.
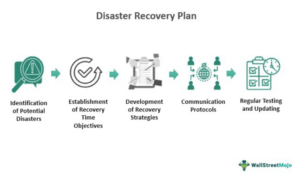
Data Backup and Disaster Recovery
Regularly backing up your data and implementing a robust disaster recovery plan are essential for maintaining business continuity and protecting against data loss. Cloud security architecture should include strategies for securely backing up data, testing backup and recovery processes, and ensuring that backups are stored in geographically diverse locations.
Employee Security Awareness Training
Human error remains one of the leading causes of security incidents. Providing regular security awareness training to your employees helps educate them about the risks, best practices, and their responsibilities in maintaining a secure cloud environment. By promoting a culture of security awareness, organizations can minimize the likelihood of accidental data breaches.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Complying with industry regulations and standards is a crucial aspect of cloud security architecture. In this section, we will explore the compliance requirements that organizations need to adhere to when operating in the cloud. We will discuss GDPR, HIPAA, and other relevant regulations, and provide guidance on ensuring compliance.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is a comprehensive privacy regulation that applies to organizations handling the personal data of European Union (EU) citizens. Cloud service providers and their customers must ensure that their cloud environments adhere to the requirements of the GDPR, such as data protection, consent management, and breach notification.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) sets forth regulations for the protection of electronic health records and personal health information. Organizations in the healthcare industry must ensure that their cloud environments meet the stringent security and privacy requirements outlined in HIPAA. This includes implementing safeguards to protect patient data, conducting regular risk assessments, and ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of health information.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) applies to organizations that handle credit card transactions. Cloud service providers and their customers must comply with PCI DSS requirements to ensure the secure handling, processing, and storage of credit card data. This includes implementing strong access controls, network segmentation, encryption, and regular security testing and monitoring.
Other Industry-Specific Regulations
Various industries have specific regulations and compliance requirements that organizations must adhere to when operating in the cloud. For example, financial institutions must comply with regulations such as the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), while government agencies must meet the standards set forth by the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP). It is essential for organizations to understand and address the specific regulatory requirements that apply to their industry.
Cloud Security Architecture Case Studies
Learning from real-world examples can provide valuable insights into the implementation of cloud security architecture. In this section, we will examine case studies of organizations that have successfully designed and implemented secure cloud infrastructures. By studying these examples, you can gain practical knowledge and inspiration for your own projects.
Case Study 1: Netflix
Netflix, the popular streaming service, has successfully built a secure cloud infrastructure to support its massive user base. They have implemented a robust identity and access management system, incorporating multi-factor authentication and role-based access controls. Netflix also relies on data encryption and continuous monitoring to protect their users’ data and ensure the availability of their service. By adopting a defense-in-depth strategy and leveraging the capabilities of their cloud service provider, Netflix has established a highly secure and scalable cloud environment.
Case Study 2: Capital One
Capital One, a leading financial institution, has embraced cloud computing while prioritizing security. They have implemented a comprehensive cloud security architecture that includes strong encryption, network segmentation, and regular vulnerability assessments. Capital One also leverages automation and machine learning technologies to detect and respond to potential security incidents in real-time. By combining advanced security measures with a proactive approach to risk management, Capital One has built a secure and agile cloud infrastructure.
Case Study 3: Airbnb
As a global hospitality marketplace, Airbnb handles a vast amount of sensitive customer data. They have implemented a robust cloud security architecture that focuses on protecting user data, ensuring secure authentication and authorization, and maintaining regulatory compliance. Airbnb employs encryption to protect data at rest and in transit, and regularly conducts security audits and assessments. By prioritizing the security of their cloud environment, Airbnb has gained the trust of millions of users and established themselves as a leader in the sharing economy.
Emerging Trends in Cloud Security Architecture
The field of cloud security architecture is constantly evolving, driven by emerging technologies and new threats. In this section, we will explore the latest trends and developments in cloud security, from container security to zero-trust architectures. Staying up to date with these trends is essential to maintain the security of your cloud environment.
Container Security
Containers have gained popularity for their ability to provide lightweight, isolated environments for running applications. However, securing containerized environments presents unique challenges. Organizations are adopting container security solutions that include vulnerability scanning, image integrity verification, and runtime protection to ensure the security of their containerized applications and prevent attacks such as container escape and privilege escalation.
Zero-Trust Architectures
Traditional perimeter-based security models are no longer sufficient in the cloud era. Zero-trust architectures assume that no user or device should be trusted by default, regardless of their location within the network. Organizations are adopting zero-trust principles, such as strong authentication, continuous monitoring, and granular access controls, to protect their cloud environments from insider threats and external attacks.
Cloud-native Security
Cloud-native security focuses on securing applications and workloads that are designed specifically for cloud environments. It involves leveraging the capabilities of cloud service providers and adopting security measures that are tailored to the cloud-native architecture. Organizations are embracing cloud-native security tools and practices, such as serverless security, micro-segmentation, and cloud workload protection platforms, to enhance the security of their cloud-native applications.
Cloud Security Architecture Tools and Solutions
In this section, we will introduce you to a range of tools and solutions that can assist you in implementing and managing your cloud security architecture. From intrusion detection systems to security information and event management (SIEM) tools, we will provide an overview of the options available to enhance your security posture.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
Intrusion detection and prevention systems play a crucial role in detecting and mitigating security threats in real-time. These systems monitor network traffic, identify suspicious activities, and take proactive measures to prevent attacks. Cloud-based IDPS solutions offer scalability and flexibility, enabling organizations to protect their cloud environments effectively.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Tools
SIEM tools collect and analyze security event data from various sources, providing organizations with comprehensive visibility into their cloud environment. These tools enable the correlation and analysis of security events, detection of anomalies, and timely response to potential security incidents. Cloud-based SIEM solutions offer centralized security monitoring and intelligence, making them well-suited for cloud environments.
Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs)
CASBs act as intermediaries between cloud service providers and cloud users, providing organizations with visibility and control over their cloud usage. These solutions allow organizations to enforce security policies, monitor cloud activity, and protect data in the cloud. CASBs offer features such as data loss prevention, encryption, and access controls, helping organizations secure their cloud environments.
Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPPs)
CWPPs are designed to protect the workloads and applications running in cloud environments. These platforms provide visibility into the security posture of cloud workloads, detect and respond to threats, and enforce security policies. CWPPs offer features such as vulnerability management, runtime protection, and workload integrity monitoring, helping organizations secure their cloud workloads.
Training and Certifications in Cloud Security Architecture
Developing expertise in cloud security architecture is crucial for professionals in the field. In this section, we will explore various training programs and certifications that can help you enhance your knowledge and skills. Whether you are an aspiring cloud security architect or an experienced professional, we will guide you towards valuable educational resources.
Cloud Security Certifications
Obtaining cloud security certifications can demonstrate your expertise and commitment to maintaining a high standard of security in cloud environments. Certifications such as the Certified Cloud Security Professional (CCSP), Certified Cloud Architect (CCA), and Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) provide comprehensive coverage of cloud security concepts, best practices, and technologies.
Vendor-Specific Training
Cloud service providers offer training programs and certifications that focus on their specific cloud platforms and security features. Providers such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer training courses and certifications that cover various aspects of cloud security architecture. These vendor-specific certifications can enhance your knowledge of the specific security tools and services offered by each provider.
Industry Conferences and Workshops
Attending industry conferences and workshops on cloud security architecture can provide you with valuable insights, networking opportunities, and access to the latest trends and technologies. Conferences such as the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) Congress, RSA Conference, and Black Hat offer a platform for learning from industry experts, sharing experiences, and staying updated on the latest advancements in cloud security.
Future Outlook of Cloud Security Architecture
In this final section, we will discuss the future outlook of cloud security architecture, considering the evolving technology landscape and emerging threats. We will explore the potential challenges and opportunities that lie ahead, enabling you to prepare for the future and stay ahead of the curve.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies are increasingly being adopted in cloud security to augment human capabilities and improve threat detection and response. AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and detect anomalies that may indicate security breaches. These technologies have the potential to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of cloud security architecture in the future.
Quantum Computing and Cryptography
The emergence of quantum computing poses both challenges and opportunities for cloud security architecture. Quantum computers have the potential to break conventional cryptographic algorithms, necessitating the development of quantum-resistant encryption methods. Cloud security architects will need to adapt their strategies and incorporate quantum-resistant cryptography to ensure the long-term security of their cloud environments.
Continued Focus on Compliance and Privacy
The increasing emphasis on data privacy and regulatory compliance will continue to shape cloud security architecture in the future. Stricter regulations and heightened consumer expectations for privacy will require organizations to implementenhanced security measures and robust privacy controls in their cloud environments. Cloud security architects will need to stay informed about evolving compliance requirements and adapt their architecture accordingly to ensure compliance and protect sensitive data.
Integration of DevOps and Security
The integration of DevOps practices and security will become increasingly important in cloud security architecture. DevOps teams are responsible for rapidly deploying and updating applications, and security needs to be seamlessly integrated into the development and deployment processes. Cloud security architects will need to collaborate closely with DevOps teams to ensure that security controls are built into the infrastructure and applications from the beginning, rather than being retrofitted.
Automation and Orchestration
Automation and orchestration technologies will continue to play a significant role in cloud security architecture. Automating routine security tasks, such as vulnerability scanning and patch management, can improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error. Additionally, orchestrating security controls across multiple cloud environments and integrating them with other security tools can provide a holistic and centralized view of the security posture.
Threat Intelligence and Sharing
As the threat landscape continues to evolve, threat intelligence and sharing will become crucial in cloud security architecture. Organizations will need to actively participate in threat intelligence communities and share information about emerging threats and attack techniques. By leveraging threat intelligence, cloud security architects can proactively identify potential risks and strengthen their security measures to mitigate them.
Cloud-Native Security Solutions
The development of cloud-native security solutions will drive innovation in cloud security architecture. Cloud service providers and third-party vendors will continue to introduce specialized security tools and services designed specifically for cloud environments. These solutions will provide organizations with more granular control, enhanced visibility, and better integration capabilities to secure their cloud resources effectively.
In conclusion, cloud security architecture is a critical aspect of ensuring the protection and integrity of data and applications in the cloud. By understanding the fundamental principles, key components, and best practices, organizations can build a robust and resilient security framework for their cloud environments. It is essential to stay informed about emerging trends, adopt innovative security solutions, and maintain compliance with industry regulations to stay one step ahead of evolving threats. As technology continues to advance, cloud security architecture will continue to evolve, requiring organizations to adapt and enhance their security measures to protect their valuable assets in the cloud.